Your server room may be somewhat intimidating to consider. Wires everywhere, mechanical boxes that just sit there, lights blinking intermittently, and the distinct feeling that you probably shouldn’t touch anything – not even a proxy server, whatever that is. However, to help you get to know your tech, the proxy server is exactly what we discuss below!
What Is A Proxy Server?
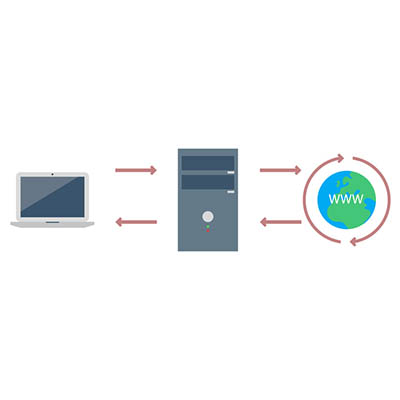
Oversimplifying things, a proxy server is the device that keeps your end users and the websites that they’re accessing separate, but communicating. Making this a little less straightforward, a proxy server can act as many other things as well, adding to its usefulness in your business.
At its core, a proxy server is extremely useful as a kind of gatekeeper for your users’ browsing. Think of it as a kind of a spam filter for your Internet – instead of a user accessing a potentially infected website, the proxy server allows them to access the data, protecting your network much like a web filter and firewall would. The proxy server also caches the data from common web requests, speeding them up, all the while preserving a user’s privacy online.
A Few Benefits of a Proxy Server
There are a few reasons that a business may utilize a proxy server.
Privacy and Security – As we’ve mentioned, proxy servers have a definite use as a means to protect an organization’s privacy and security. This can be accomplished in a few ways. First, a proxy server is capable of altering some of the identifying information contained in the web request. By its doing so, the destination server has no way of knowing where the request came from originally. This keeps browsing habits and personal information protected.
Furthermore, a proxy server is able to encrypt web requests, protecting them from anyone who may try to sneak a peek. Known malware sites can also be blocked through the proxy server. Finally, your company can use a virtual private network (or VPN) in conjunction with the proxy, enabling secure and verified access.
Internet Control – Let’s face it, as great a tool as the Internet is, it can also be a considerable source of distractions. However, a proxy server allows you to both monitor and control the way the Internet is used. If certain websites are proving to be a distraction, the proxy server can block them, instead delivering the user a nice note reminding them to stay on task. Even if the website isn’t blocked, a proxy server can still be used to track how often a website is accessed, allowing you to judge if your employees are really being diligent in their work.
Speeds and Savings – Bandwidth is a very important consideration to make when your business relies on the Internet’s performance in order to function. A proxy server can assist your network performance by caching websites that are frequently visited, cutting the number of requests to that website to one, as opposed to however many employees are attempting to access it.
If you think that your network could benefit from utilizing a proxy server, call us! COMPANYNAME is the premier managed IT support specialist for AREASERVED, and we are more than ready to assist you with whatever questions you may have. Give us a call today at PHONENUMBER.